On-Demand OS: Where Agents drive your smartdevices [AI Generated PRD]
This is an AI generated PRD (GPT 4.5) that explores the concept of an AI-driven operating system. While On-Demand OS is currently a theoretical model, elements of this approach are beginning to appear in various mobile platforms and AI assistants.
- Prompt given: make a prd for executing this prototype demo of On-demand OS. A phone with basic types of generative and text llms and audio llms and some basic system apps pre generated from llms (or maybe workflow templates, available on demand anytime). powerful llms running locally on phone, all data personal and encrypted locally. Say you need a calculator, not everytime you need the basic one (you can just ask that) - but complex calculations in real life, like splitting, or tips, etc - it could pull up an ui on demand to do the task. you could save this gen-app/workflow for later. there would be characterised/dedicated agents for diffferent types of task. imagine a wealth advisor, a trip planner, a personal assistant, who can make use of all these available tools locally and connect to web on demand and accomplish tasks on your behalf.
Overview
Interactive Demo by Claude 3.7
On-Demand OS is a next-generation operating system designed for flagship smartphones. It integrates powerful generative AI models running locally on the device, enabling users to generate apps, perform complex tasks, and interact with intelligent agents on demand via natural language. The system emphasizes privacy: all user data and AI interactions are encrypted and stored on the device by default, with nothing sent to the cloud unless the user explicitly permits it. This approach combines the convenience of advanced AI with robust privacy and security for the end user.
Target Audience
On-Demand OS is aimed at a broad range of users who can benefit from built-in AI capabilities:
- General Consumers: Everyday users who want a smarter phone that can create tools or content on the fly (e.g. generating a custom photo album app or getting meal plans from a personal assistant).
- Business Professionals: Power users who need productivity aids, such as an AI that can organize schedules, plan business travel, or generate reports and dashboards through simple requests.
- Developers & Tech Enthusiasts: Users who want to experiment, customize their experience, or build new applications. They benefit from on-device code generation and the ability to extend the OS with their own AI-driven workflows or apps.
Core Features & Capabilities
Generative AI Models On-Device
On-Demand OS comes with multiple embedded AI models to handle a variety of tasks without needing an internet connection for processing:
- Text-Based AI: A GPT-based language model is integrated for understanding and generating text. This acts like a built-in assistant for thoughts, answering questions, summarizing information, and carrying on conversations with the user.
- Image Generation: The OS includes DALL-E technology, allowing users to create or edit images through simple prompts (for example, "Generate a picture of a sunset over mountains" will produce a unique image on the device).
- Code Generation & Reasoning: A state-of-the-art AI model (Claude 3.7 "Sonnet") is dedicated to coding assistance and complex problem-solving. Developers can get help generating code snippets, debugging, or even having the AI reason through technical problems step by step, all locally.
These models run locally thanks to the phone's AI acceleration hardware, ensuring quick responses and maintaining user privacy (since data does not have to be sent to external servers for processing).
Intelligent System Apps & Dynamic UI Generation
The OS can dynamically create temporary apps or user interfaces on demand to fulfill specific tasks:
- Users can request custom, one-off tools and the system will generate a functional UI for it in real time. For example, a user might say, "I need a tip calculator" or "Create a personal budget planner," and the OS will instantly generate an interactive app or dashboard tailored to that request.
- These generated system apps are interactive and come with common UI components. The user can input data or adjust parameters as needed (e.g. entering bill amounts in the tip calculator or setting income/expenses in the budget planner).
- The OS provides customizable workflow templates with predefined options, so users can also choose from templates (like a project management board or a habit tracker) and then refine them to their needs.
- Any dynamically created tool or workflow can be saved for future use. This means if you generate a useful dashboard or app, you can keep it on your phone as a persistent app or shortcut, avoiding the need to recreate it every time.
This capability essentially turns the smartphone into a flexible toolbox that adapts to the user's immediate needs, creating or modifying software interfaces on the fly.
AI Agents for Task Execution
On-Demand OS includes a suite of specialized AI agents that act as personal assistants for different domains. Each agent is tailored for particular categories of tasks and can carry out complex operations by combining on-device intelligence with internet access when allowed:
- Personal Wealth Advisor: An AI agent focused on finance can help track expenses, suggest budget plans, and even give investment insights. For example, it can analyze your spending (locally, using your data), and if permitted, fetch the latest stock prices or news to advise on investments.
- Travel Planner: This agent helps plan trips or outings. You can ask it to plan a week-long vacation itinerary --- it will use local knowledge (preferences you've shared, past trips) and also gather real-time information from the web (like flight options, hotel availability, attraction hours) via APIs or safe web scraping. It then presents a draft travel plan, which you can adjust through a generated UI.
- Personal Assistant: A general-purpose assistant that can handle daily tasks such as setting up meetings, sending messages, creating to-do lists, or finding information. It might summarize your unread emails, schedule appointments by checking your calendar, or wake you up with a briefing of the day's news (retrieved from the internet if you allow).
All these agents leverage local tools first (using the phone's built-in apps, data, and AI models) and only reach out to online services when necessary and permitted. They have persistent memory during a session, meaning they remember context from previous interactions to better assist you (for instance, the travel planner recalling you prefer morning flights). However, this memory can be easily reset by the user at any time, ensuring you can wipe the context for privacy or simply start fresh with a new query.
Security & Privacy
Strong security and privacy measures are core to On-Demand OS's design:
- Local Encryption: All user data, AI model data, and interaction history are encrypted and stored locally on the device. This includes any notes you make, preferences you set, or content generated by the AI. Even if someone gains access to the raw storage, the data remains protected by encryption.
- User-Controlled Cloud Sync: By default, nothing is uploaded or synced to cloud services. Users may explicitly opt-in to sync certain data (for backup or cross-device use), but this is never done without permission. For example, you might choose to back up saved workflows or allow an AI agent to access your online calendar --- these actions are opt-in and transparent.
- Secure Execution: The generative models and AI agents run in a sandboxed environment on the device, which isolates them from sensitive parts of the OS. They only have access to the data or sensors that you grant, preventing any unauthorized data access. Regular security audits will be conducted to ensure that AI components cannot leak data or be exploited.
Overall, the OS ensures that users get the benefits of powerful AI while maintaining full control over their data. Privacy isn't just a feature but the default state.
Web Connectivity & External Data Access
While On-Demand OS emphasizes offline and on-device functionality, it is also equipped to smartly use internet resources when needed, under the user's control:
- API Integration: The OS can connect to online services through APIs to fetch real-time data. For example, if you ask an agent for the current weather or live stock prices, the OS can call weather or finance APIs to get up-to-the-minute information. This is done in a controlled manner, and you'll know when such calls happen.
- Web Scraping: If an official API isn't available for the information needed, the OS has the ability to perform web scraping to extract relevant data from websites. For instance, the travel agent might scrape a hotel website for availability if it can't get that data via API. The system ensures this is done efficiently and respects web content rules.
- Dynamic Method Selection: The OS uses a feasibility-based approach to choose the best method for each task. It will decide whether to use a local database, call an API, or perform web scraping based on factors like the type of request, the need for real-time accuracy, connectivity status, and privacy considerations. This decision process is automatic and optimized for speed and reliability, so the user doesn't have to worry about how the data is fetched.
By combining local AI with controlled web access, On-Demand OS can answer complex queries and perform tasks that require up-to-date information, all while keeping the user in the driver's seat regarding what external data is accessed.
Technical Requirements
- Hardware: On-Demand OS is intended for high-end smartphone hardware. It requires a powerful processor (latest-generation mobile CPU) with a dedicated AI acceleration unit (such as an NPU or GPU) to run the AI models efficiently. Sufficient memory (RAM) is needed to hold large models, and ample storage is required for model files and generated content. Flagship smartphones and future devices with AI chips are the primary targets for this OS.
- Software Platform: The OS is built as a custom platform optimized for on-device AI. It includes a specialized scheduler and memory manager to handle the intensive workloads of generative models. The kernel and system services are tuned to allow low-latency responses from the AI components. Additionally, the OS likely uses a lightweight hypervisor or container system to sandbox AI agents and model processes for security. Despite these advanced capabilities, the core OS remains efficient, so it can perform well on a battery-powered device without excessive power drain.
- User Experience (UX): The user interface is minimalistic and intuitive, designed so that users primarily interact through conversation or simple commands. Natural language understanding is deeply integrated --- users can open apps, adjust settings, or invoke complex workflows just by speaking or typing a request. The visual design is clean, with the dynamic UIs generated by the system following a consistent style guide for coherence. There is an emphasis on explainability in the UX as well: when an AI agent takes an action or fetches data, it can show a brief note (for example, "Fetching latest news from BBC...") so that even non-technical users feel confident about what the system is doing.
The On-Demand OS Workflow
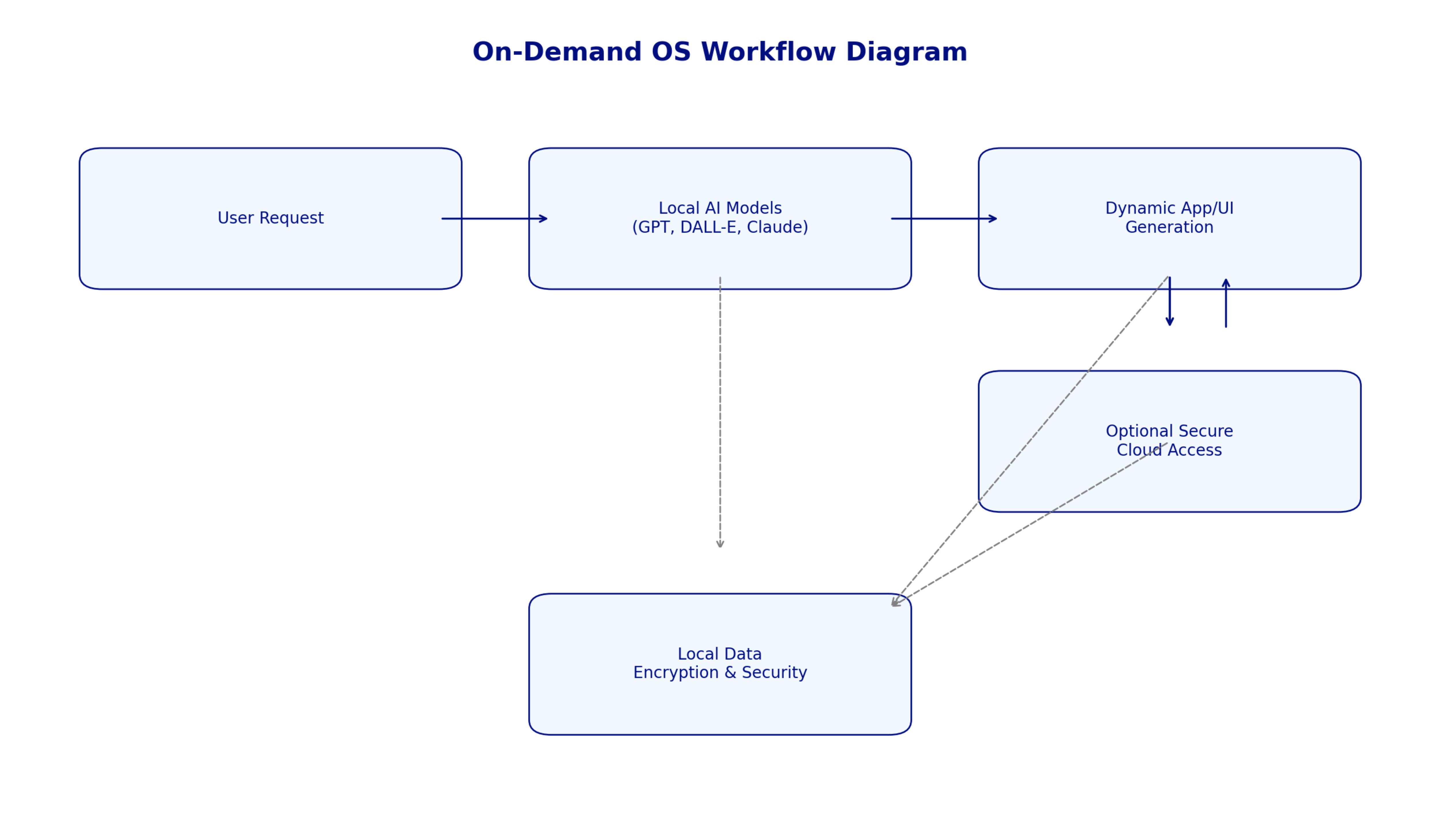
The On-Demand OS workflow from user request to dynamic interface generation
Customization & Developer Access
On-Demand OS is designed to be flexible and extensible, encouraging users and developers to tailor the AI-driven experience to their needs:
- Out-of-the-Box Workflows: The OS comes with a set of pre-built workflows and example AI-driven apps for common tasks (such as note-taking, to-do lists, basic budgeting, etc.). These serve as both useful tools and templates that users can learn from.
- User Customization: Regular users can modify existing workflows or create new ones without thoughts code. This can be done through natural language instructions (e.g., "Create a workflow that reminds me to drink water every 2 hours and logs it") or by tweaking settings in a graphical editor. The system will interpret user instructions to set up the logic and UI of a custom workflow. This empowers users to personalize their OS experience---like adding a custom health tracker or a specialized calculator---on the fly.
- Developer SDK: For developers and tech-savvy users, an SDK (Software Development Kit) will be provided. This allows deeper integration with the OS's AI capabilities. Developers can create third-party apps or agents that plug into the On-Demand OS framework, reusing the on-device models and security sandboxing. The SDK will support programming languages and tools familiar to mobile developers and will include APIs to invoke the generative text, image, and code models, as well as to define new dynamic UI templates or agent behaviors. This opens the door for an ecosystem of AI-enhanced applications and services built on top of On-Demand OS.
By offering both simple customization for non-programmers and powerful tools for developers, On-Demand OS ensures that the system can evolve with user needs and foster innovation from the community.
Potential Use Cases
On-Demand OS's features enable a wide range of practical use cases for different types of users. Below are a few scenarios illustrating how people might use this OS in daily life:
- Personal Finance Management: A user engages the built-in wealth advisor agent to help with budgeting. They simply say, "Help me plan my monthly budget." The agent then analyzes the user's spending data (securely on-device) and generates a budget planner app with a dashboard showing expenses by category. It might also fetch current interest rates or investment options via the web (with permission) to suggest how to allocate any savings. The user can adjust sliders or inputs in the generated UI (for income, savings goals, etc.), and the agent will update the recommendations in real-time.
- Travel Planning: A busy professional is planning a vacation. They tell the trip planner agent, "Plan a 5-day trip to Japan next April, I like cultural sites and good food." The AI agent gathers information: it uses APIs to find flight and hotel options, scrapes travel blogs for must-visit restaurants and historical sites, and then presents the user with an interactive itinerary UI. The itinerary app lets the user click through each day's plan, showing maps and notes. The user can tweak the plan (e.g., swap a suggested museum visit for a different one) directly in the UI, and the agent will adjust the rest of the schedule accordingly. All of this happens in a conversational manner with visual aids, without needing the user to manually search multiple websites or apps.
- Instant App Creation for Daily Needs: Imagine friends at a dinner splitting the bill. One of them pulls out a phone running On-Demand OS and says, "Create an app to split our expenses for this trip, including tonight's dinner." The OS quickly generates a bill-splitting app: a simple interface where they can enter each expense and who paid. The app calculates how much each person owes in total, factoring in all shared expenses over the trip. The group uses the app on the spot, and when done, they save it so they can reuse it on the next group trip. This saves time and avoids downloading a dedicated app or doing the math manually.
- Coding and Debugging on the Go: A software developer is away from their computer but has an idea for a piece of code. They open the On-Demand OS code assistant and describe what they want: "Generate a Python function that sorts a list of numbers using quicksort." The Claude-based coding agent produces the code instantly and even explains how it works in plain language. Later, the developer encounters a bug in a script. They paste the code into the assistant on the phone and ask for help. The AI analyzes it, identifies the issue, and suggests a fix. This all happens offline, so sensitive code never leaves the device --- a big plus for proprietary projects.
- Everyday Personal Assistant Tasks: A user relies on the personal assistant agent throughout the day. In the morning, they say, "Good morning," and the phone greets them with a summary of the day: the agent compiled the user's calendar appointments (from the local calendar app or a synced work calendar if allowed), the weather forecast, and news headlines. During the day, the user can ask, "Remind me to call John when I get home," and a reminder workflow is automatically created. If the user gets a text in French, they can ask the agent to translate it; it does so using the local GPT model. In all these cases, the interactions are natural and conversational, and the user doesn't have to juggle multiple apps --- the assistant coordinates everything under the hood.
These examples showcase how On-Demand OS can streamline tasks in various scenarios, whether it's for personal life, work, or creative endeavors. The common thread is that the user can simply ask the OS for what they need and the system will handle the rest, by generating apps, fetching information, or delegating to the appropriate AI agent.
Next Steps
To bring On-Demand OS from concept to reality, the following steps are planned:
- Prototype Development: Begin building a prototype focusing on the core features. For example, implement a basic version of one or two AI agents (like the personal assistant and the UI generator) running on a high-end smartphone. This also involves integrating a GPT-based model and DALL-E on-device and demonstrating a simple dynamic app generation (perhaps the tip calculator scenario). The prototype will help validate the feasibility of running these models locally and refine the user experience for interacting with them.
- Performance Benchmarking: Rigorously test and optimize the on-device AI models. This step will measure how quickly the models respond on typical flagship hardware, how much battery they consume, and how much memory they use. Various scenarios (text generation, image creation, code assistance) will be benchmarked. The goal is to ensure a smooth experience --- for instance, aiming for sub-2-second responses for text queries and reasonable generation times for images. Based on results, the team may compress models or use quantization techniques to improve efficiency without significantly sacrificing capability.
- Security Auditing: Conduct a thorough security review of the entire system. This includes ensuring the encryption of local data is robust and has no backdoors, verifying that AI agents cannot access data they shouldn't (each agent should follow permission rules), and testing the cloud sync mechanism to make sure data only leaves the device when it's supposed to. External security experts might be brought in to perform penetration testing on the OS, especially focusing on the new AI components and their interfaces. Any vulnerabilities found will be addressed, and encryption implementations will be verified for compliance with industry standards.
- User Testing & Feedback: (Parallel to the above steps) Recruit a small group of beta users (covering both tech-savvy users and non-technical users) to try out the prototype. Their feedback on usability, clarity of the AI's actions, and overall satisfaction will be gathered. This will guide UI improvements, help refine how the OS explains its actions to users, and identify any confusing aspects of the dynamic app generation process.
By following these steps, the development team will ensure that On-Demand OS is not only feature-complete and innovative, but also performant, secure, and user-friendly when it launches. The result will be an operating system that truly augments the smartphone experience with on-demand intelligence, while keeping the user in full control.